Music and memory form an omnipresent cultural artifact, tightly entwined with human emotion and history, creating a tapestry of auditory legacy that spans across lifetimes and civilizations. This profound relationship transcends mere entertainment, positioning music as a vital part of our identity and personal history. As we explore the depths of how melodies and rhythms shape our experiences, we uncover the enduring power of music to sustain memories, offering both solace and a sense of identity through the harmonious rhythms of life.
Historical Perspective
From ancient tribes using rhythmic drumming in sacred ceremonies to the grand orchestras of the Baroque period echoing in the halls of Versailles, music has served as a cornerstone of societal rituals and personal solace. This historical journey of music illustrates its profound impact on collective memory across generations.
Music Therapy: An Overview
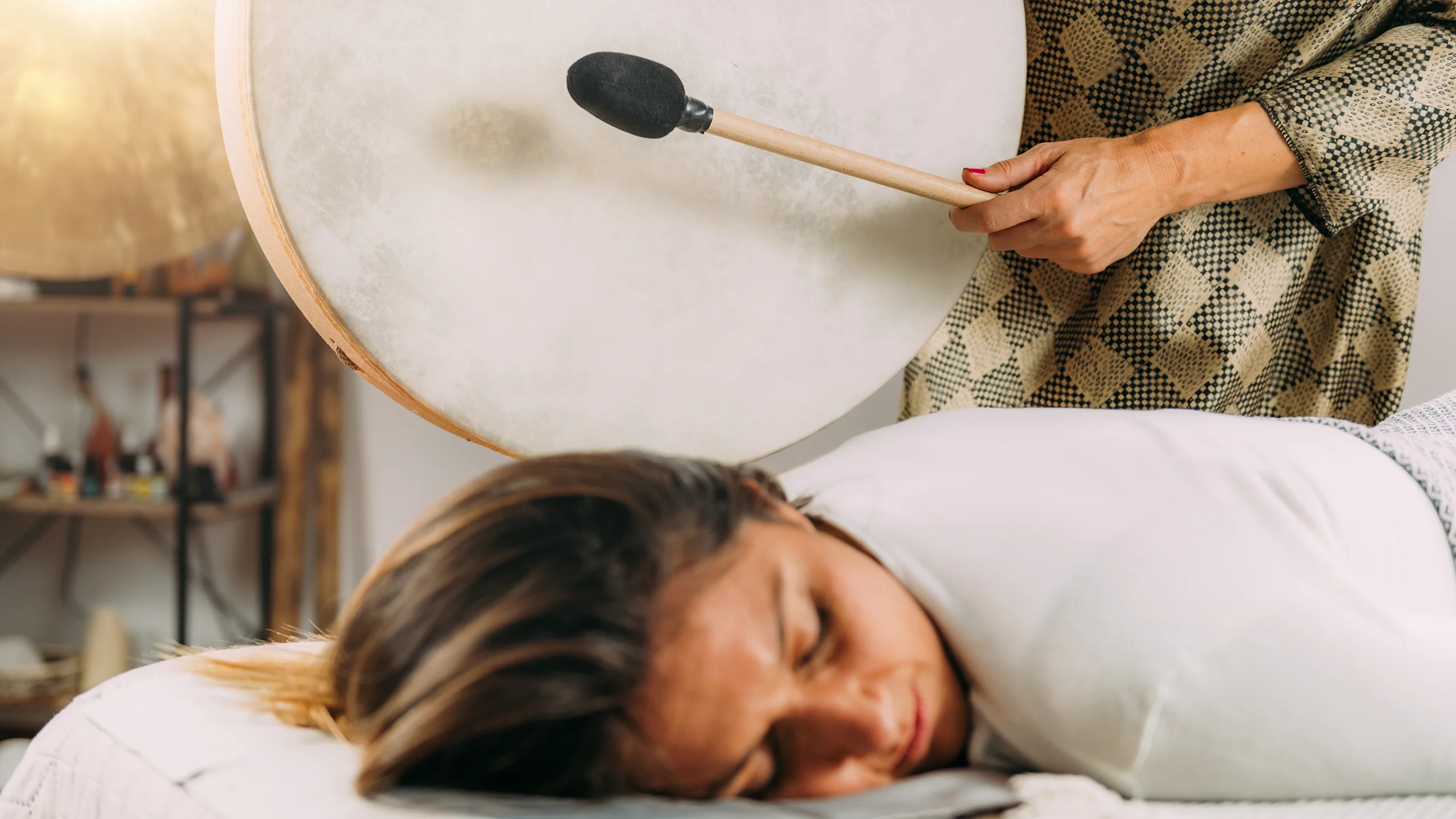

Music therapy emerges as a structured practice, using the inherent qualities of musical interventions to heal and restore mental health. Through case studies, such as those involving individuals overcoming trauma, the therapeutic prowess of music is celebrated. Furthermore, rhythm and tempo play significant roles, acting as a scaffold for memory retrieval. This allows individuals to recall not only the music itself but also the associated experiences and emotions, which are often vivid and rich in detail. Such dynamic interplay between music and memory offers promising insights into therapeutic applications, especially for patients with memory impairments.
The Science of Sound and Recall
Neurologically, music functions as a profound catalyst, engaging extensive networks of neurons that are crucial for evoking and enhancing memory. When we listen to music, specific brain structures are activated, particularly those associated with emotional processing and memory retention, such as the amygdala and the hippocampus. Melodies harness the brain’s unique ability to synchronize rhythm and recall, creating robust links between auditory cues and episodic memories. This auditory processing is not merely about hearing a tune; it involves the intricate coordination of these brain centers to reconstruct contexts, emotions, and scenes associated with the musical piece.
Psychological Impacts

The psychological landscape of music is vast, with its ability to evoke the most profound emotions and vivid memories. For example, the joy of a wedding dance can instantly transport us back to that moment of happiness and celebration, illustrating how music anchors life’s milestones in our minds. Music can also play a crucial role in mood regulation, offering a therapeutic respite for those feeling anxious or stressed. Studies have shown that certain melodies can stimulate the production of neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin, which enhance feelings of well-being and can even alleviate symptoms of depression. Moreover, familiar tunes can reinforce cognitive function and social connection, particularly in older adults, making music a powerful tool for maintaining psychological health as we age.
Memory Disorders and Music
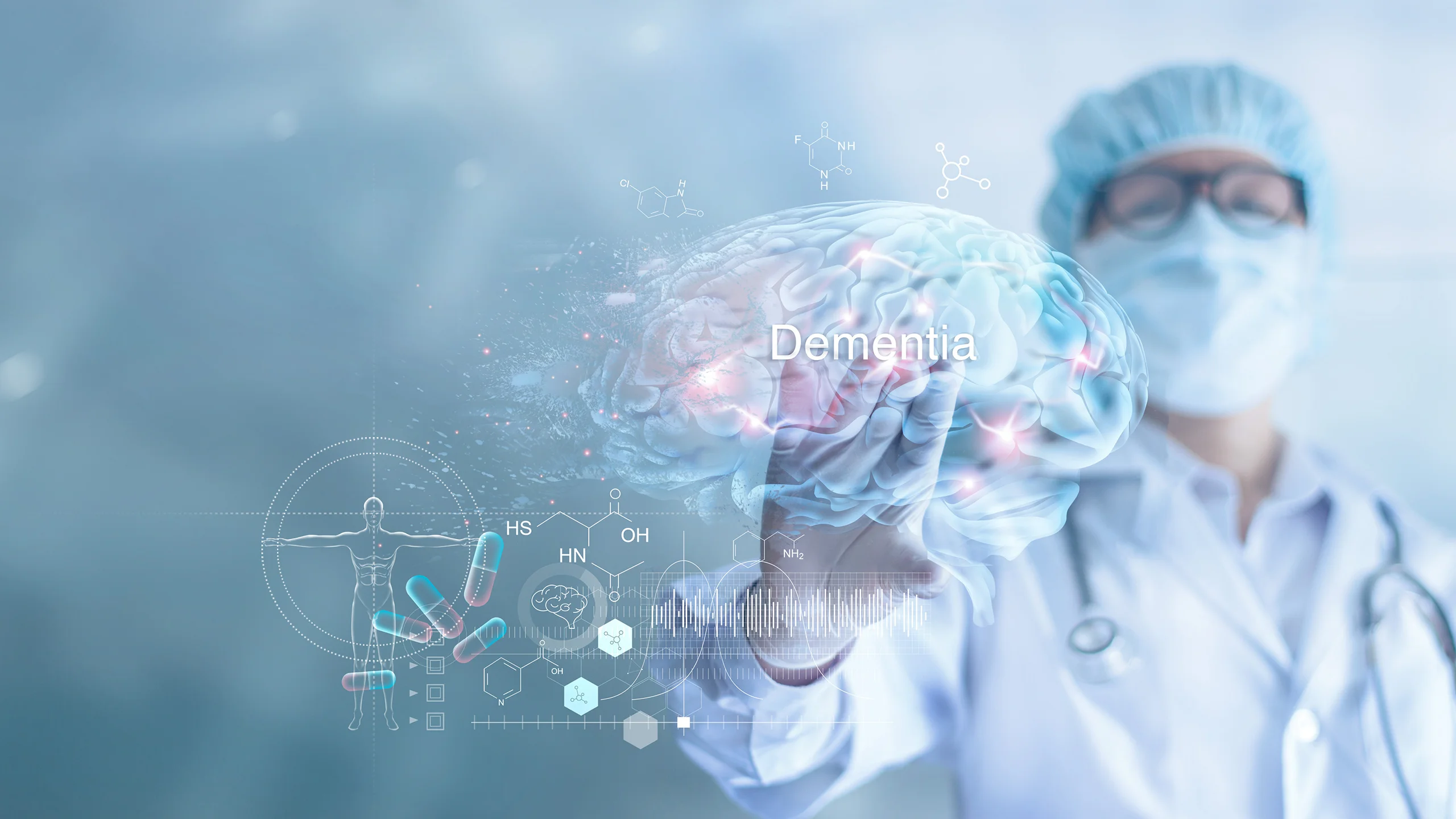

In the realm of memory care, music has shown remarkable efficacy, particularly among dementia patients. It not only soothes agitation but also revives memories, providing comfort and connection to those seemingly lost to their illness.
Cultural Dimensions of Music Memory
Globally, music serves as a repository of cultural history, preserving the heritage and collective memory of communities. Whether through folk songs or sophisticated symphonies, each note carries the weight of ancestral voices.
Children and Music Education
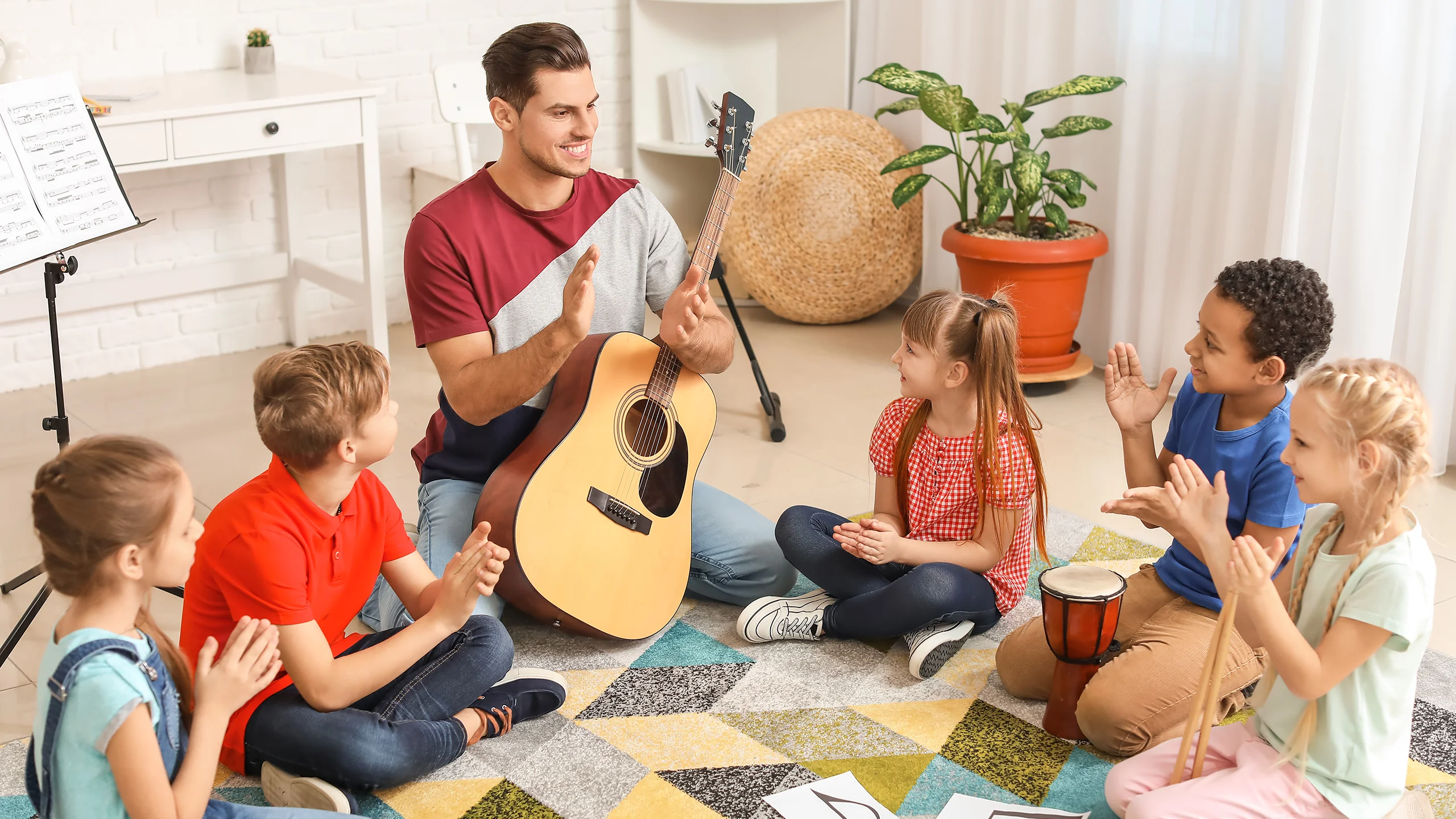

Educationally, the introduction of music to children’s lives plays a pivotal role in fortifying their cognitive abilities, significantly enhancing memory, and facilitating learning through playful, musical engagement. Engaging with music helps young learners develop language skills, improves their ability to concentrate, and strengthens mathematical abilities through rhythm and beat recognition. Furthermore, music fosters emotional development by helping children express themselves and manage their feelings through creative outlets. Group musical activities promote social skills by teaching children about teamwork and respect for others’ contributions.
Music in Everyday Life
Integrating music into daily routines can significantly boost mental energy and focus, making mundane tasks more enjoyable and productive. Background music has been proven to enhance cognitive performance and memory retention in workplace and academic settings.
Music and Aging
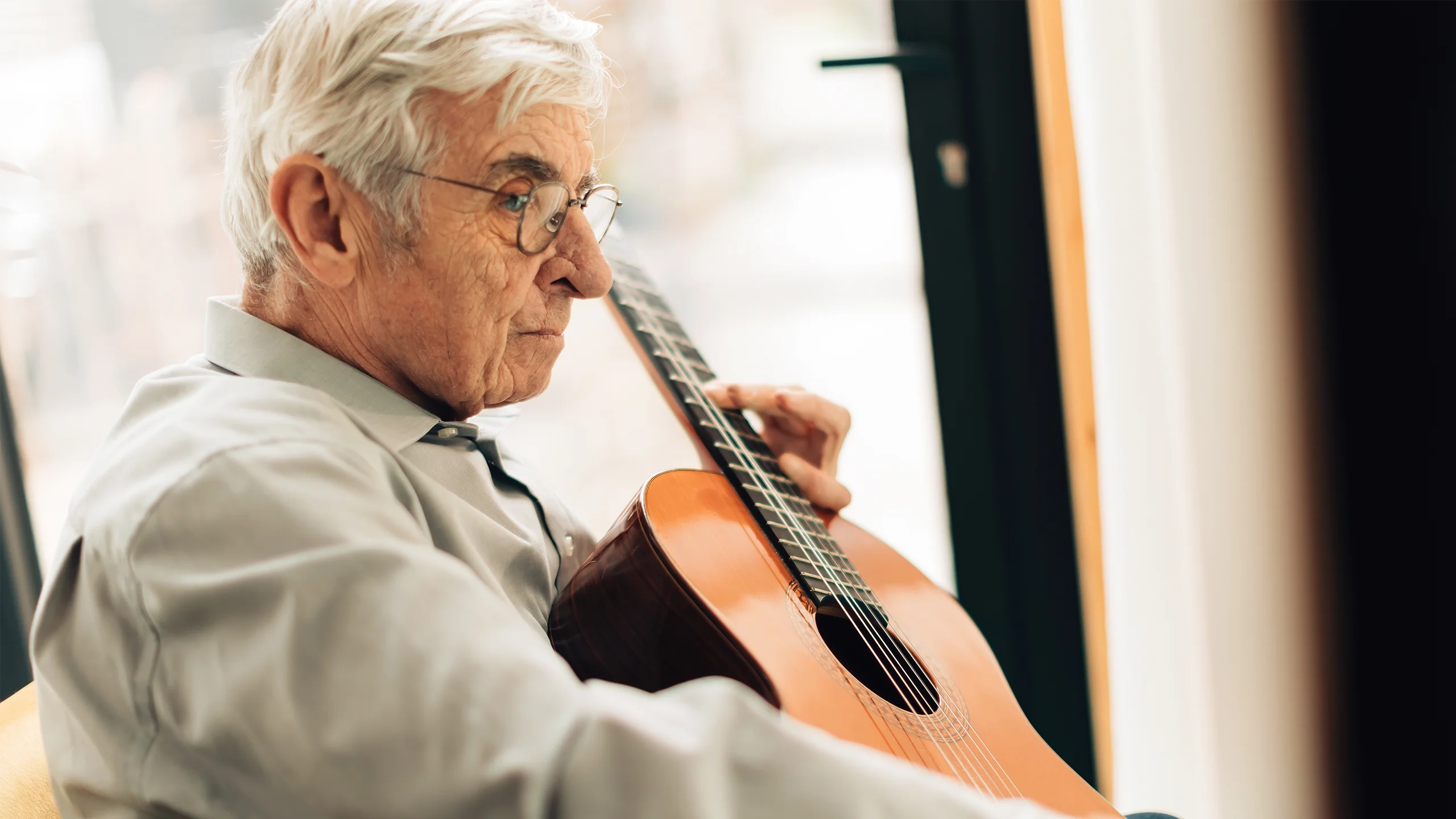

As we age, our musical tastes and the memories associated with them evolve, yet the foundational impact of familiar tunes remains, often providing comfort and a sense of identity in later years. Music often plays a pivotal role in community events, serving as a vehicle for preserving and transmitting collective memories, thereby strengthening community bonds.
The Role of Musicians in Memory-Making
Musicians and composers significantly influence our collective memory, creating soundscapes that resonate deeply with listeners. Their creative processes involve careful selection of melody, harmony, and rhythm to enhance thematic elements and evoke strong emotional responses. By embedding narrative elements into their music, artists forge a personal connection with the audience, ensuring memorable and impactful experiences. Through their work, musicians not only craft the soundtrack for key life moments but also shape personal and cultural narratives, highlighting their profound role in memory-making.
Methodologies in Music and Memory Research
The exploration of the intricate relationship between music and memory continues to advance, with researchers employing innovative methodologies to uncover deeper insights. Recent studies in this field are revealing fascinating aspects of how music influences brain function and memory retention:
Neuroimaging Techniques:
Advanced imaging technologies like fMRI and PET scans allow scientists to observe real-time brain activity when individuals engage with music. This research has highlighted areas in the brain that are activated by musical exposure, showing how these areas are linked to emotional processing and memory storage.
Longitudinal Studies on Music Therapy:
Ongoing studies track the effects of regular musical engagement on individuals with cognitive disorders. For example, research involving Alzheimer’s patients has shown that those regularly exposed to music exhibit slower cognitive decline compared to those who are not.
Experimental Designs Using Virtual Reality:
Combining music with virtual reality technology offers a new dimension to studying memory. Researchers are using VR to simulate environments tied to specific musical memories, helping to understand how context and music recall are connected.
Cross-Cultural Research:
Comparative studies across different cultures examine how diverse musical traditions impact memory. These studies help to identify universal patterns as well as culturally specific responses to music.
These methodologies not only deepen our understanding of how music functions as a mnemonic device but also pave the way for developing more effective therapeutic interventions for memory enhancement.
Practical Tips for Integrating Music into Memory Exercises

Integrating music into daily routines can be a delightful and effective way to enhance memory. For individuals seeking to harness the power of music for personal cognitive enrichment, the following practical tips can guide the selection of genres and pieces that promote cognitive activity and emotional recall:
Create a Memory Playlist:
Compile songs that have personal significance or evoke strong memories. Listening to this playlist can help reinforce these memories and stimulate emotional recall.
Engage with Classical Music:
Studies suggest that classical music, particularly pieces with a clear structure like those from Mozart or Bach, can enhance mental focus and memory retention.
Use Music as a Background for Learning:
Play instrumental music softly while studying or learning new information to improve concentration and memory consolidation.
Sing Along to Improve Recall:
Singing along to familiar songs can enhance verbal memory and the ability to recall information.
Incorporate Rhythmic Elements:
Use rhythmic patterns and beats to memorize lists or sequences. Crafting short songs or jingles can make the process of remembering everyday information more fun and efficient.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the symphony of music and memory resonates through every chapter of human life, from the earliest melodies heard in childhood to the nostalgic tunes that echo in our later years. This intricate relationship enhances our daily experiences and emotional well-being and also holds profound therapeutic potential for those facing memory-related challenges. Music’s capacity to connect, soothe, and invigorate is unparalleled, making it a timeless tool for personal development and communal harmony. As we move forward, the confluence of music, science, and technology promises even greater insights and innovations, ensuring that music continues to play a vital role in shaping our memories and defining our collective identities. This ongoing journey into the depths of music and memory invites us to appreciate the sounds of the present and not forget to forge lasting legacies for the future.
If you would like to learn more about music and boosting senior wellness with singing, click the link below to be taken to another article that talks about exactly that!
Boosting Senior Wellness with Singing – HeartString Harmonies




Leave A Comment